Simulation of photovoltaic system production is an important tool for project design and economic assessment. Using the example of three PV plants in the Czech Republic, we show that there can be differences of more than 10% between simulation and reality. The accuracy of the simulation is influenced by the input data, model settings, and actual operation. When used correctly, simulation is a valuable aid. In practice, however, it is important to understand its limitations and not underestimate deviations that can have a significant impact on the financial return of the project. Even so, PV plant production simulation is one of the main tools in the planning and design of photovoltaic power plants.
Methodology for comparing PV simulation and reality
To verify the accuracy of the prediction, three photovoltaic power plants located in different parts of the Czech Republic were inspected. These power plants are designated FVE 1, FVE 2, and FVE 3.
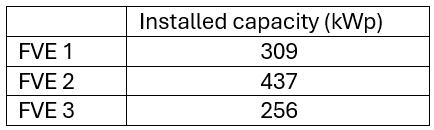
Annual fulfilment of simulated PV values
The graph shows that the results of individual power plants vary in terms of annual production, but all exceed 90%. This variation shows that even when using the same simulation model and identical input parameters, the results may differ. The final production is influenced by the actual operating conditions of each specific power plant, such as the local microclimate, the slope and orientation of the panels, or the level of maintenance.
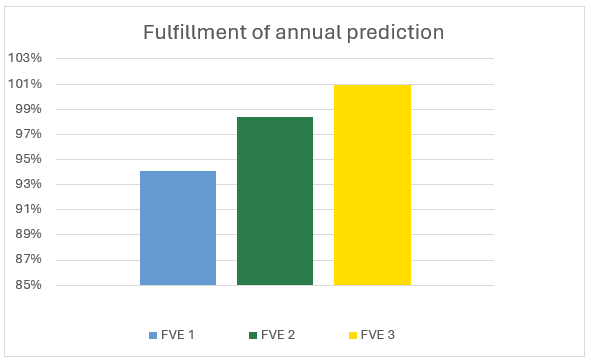
Monthly development and seasonal deviations
The graph shows that the actual fulfilment of simulated production varies between the monitored PV plants in individual months.
- In winter (January, February, and December), some power plants reach 70–80%, while others exceed 90%.
- The summer months (May–August) show stable performance of around 90–110% for all PV plants, which corresponds well with the simulation.
Overall, it is clear that monthly deviations are not random but reflect real local influences that are not fully captured in simulations – in particular, short-term climatic phenomena, system maintenance, or differences in panel orientation.
Benefits and limitations of PV production simulation
Advantages of using simulation:
- Detailed analysis of production according to specific power plant parameters,
- Possibility to optimise system configuration prior to installation,
- Standardised outputs recognised by banks and subsidy authorities.
Main disadvantages and limitations:
- Dependence on the quality of climate inputs (e.g., irradiation from databases),
- Simplified model of operating conditions – it can never accurately predict what a given year will look like in terms of weather, power plant outages, pollution, etc.